This article is a summary version of UB Ventures’ “SaaS Annual Report 2023-2024,” which provides an overview of the Japanese SaaS market and trends in 2023.
The full report (24 pages) can be downloaded from the form at the bottom of this article.
On publication of the SaaS Annual Report
Osamu Iwasawa, Managing Partner, UB Ventures
In 2024, Japan’s top listed SaaS company exceeded JPY 30 billion in ARR (subscription revenue). Although many investors saw weak valuations and divested from SaaS, fundamentals demonstrate increasing strength. It is no exaggeration to say that SaaS has already become an established industry in Japan.
The key factors driving growth are multi-product offering and expansion of sales to large enterprises and SMEs.
Top SaaS companies pursuing a multi-product strategy have been aggressively engaging in M&As, with a number of deals in 2023.
In the enterprise domain, companies are providing more labor-intensive solutions, such as BPaaS (Business Process as a Service), which includes customizable ERP and consulting services, to meet the needs of large-scale customers that support higher unit prices.
We are also noticing an increase in vertical SaaS products that tackle social issues in a uniquely Japanese context, rather than replicating existing solutions in the United States.
Japan is facing the world’s fastest population decline, and a labor shortage in essential legacy industries such as construction, manufacturing, and logistics has become a social issue.
With a choice between increasing the workforce and improving productivity per worker, expectations for vertical SaaS to improve productivity in legacy industries are becoming even higher.
This report consists of three sections: “Overview” is a summary of the latest data on the SaaS market; “Vertical SaaS” provides an analysis of growth drivers in the rapidly growing vertical SaaS market; and “Depopulating Society” is a deep dive into key topics in a declining population.
I hope that this report will reach many readers to provide insight into emerging themes.
<Overview>
The SaaS industry continues to show strong growth, with a variety of developments in 2023.
In order to provide a bird’s-eye view of the ever-changing industry, we have compiled an overview of quantitative analysis from various perspectives, including ARR, multiples, IPOs, private equity, M&A, and ARR acquisition efficiency.
Here, we excerpt selected parts of the report and provide commentary.
1. ARR: Listed SaaS companies in Japan are reaching ARR JPY 30 billion. Top players offer multiple products to maintain growth.
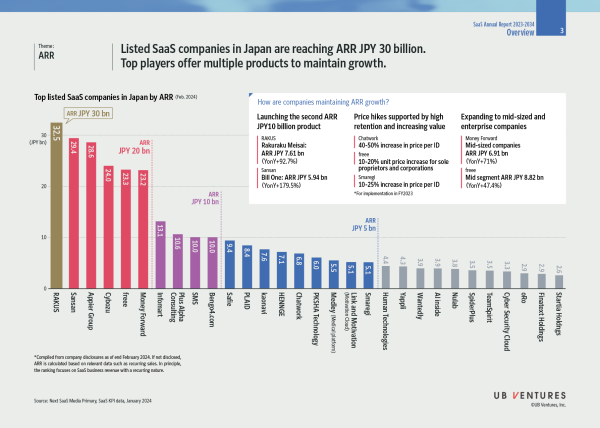
ARR, which indicates the scale of SaaS businesses, is reaching JPY 30 billion, led by RAKUS. Top SaaS companies are showing strong growth without diminishing growth rates, with growth drivers such as multi-product offering, unit value improvement through price hikes, and expansion into the mid-size and enterprise domains.
2. Valuation: Average PSR remains at 6-8x since 2022. Profit was a clear valuation factor in 2023.
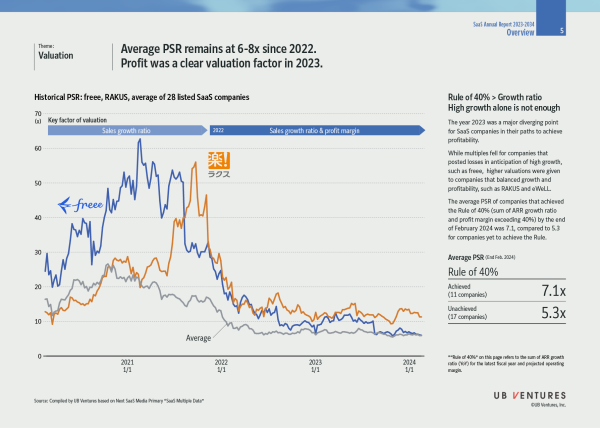
The year 2023 was a major diverging point for SaaS companies in their paths to achieve profitability. While multiples fell for companies that posted losses in anticipation of high growth, such as freee, higher valuations were given to companies that balanced growth and profitability, such as RAKUS and eWeLL.
The average PSR of companies that achieved the Rule of 40% (sum of ARR growth ratio and profit margin exceeding 40%) by the end of February 2024 was 7.1, compared to 5.3 for companies yet to achieve the Rule.
3. Rule of 40%: The sum of ARR growth rate and profit margin should exceed 40% to qualify for high valuations. Earnings forecasts are shifting focus from growth to profitability.
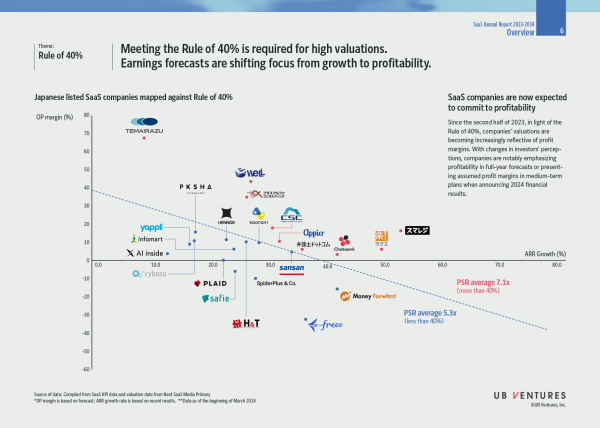
Since the second half of 2023, in light of the Rule of 40%, companies’ valuations are becoming increasingly reflective of profit margins. With changes in investors’ perceptions, companies are notably emphasizing profitability in full-year forecasts or presenting assumed profit margins in medium-term plans when announcing 2024 financial results.
4. M&A: 2023 saw a record number of M&As involving SaaS startups.
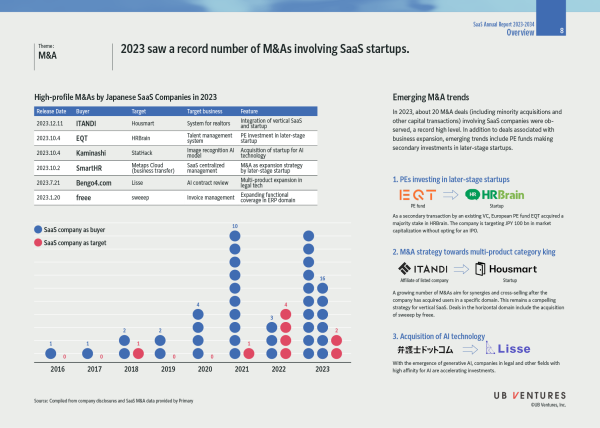
In 2023, about 20 M&A deals (including minority acquisitions and other capital transactions) involving SaaS companies were observed, a record high level. In addition to deals associated with business expansion, emerging trends include PE funds making secondary investments in later-stage startups.
5. Startup Fundraising: The amount and cases of SaaS startup investment decreased. SaaS accounted for 18% of startup investment in Japan.
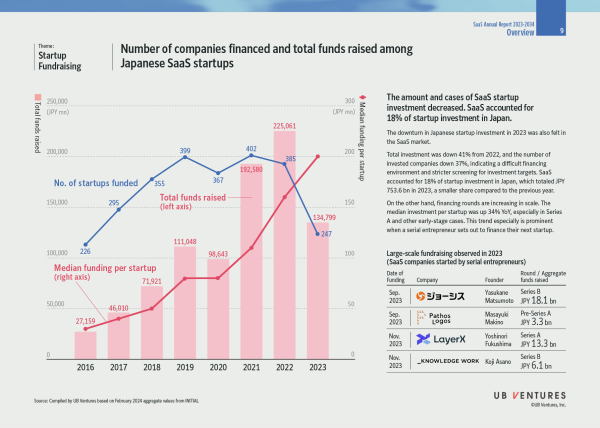
The downward trend in domestic startup investment in 2023 was also seen in the SaaS space.
The downturn in Japanese startup investment in 2023 was also felt in the SaaS market.
Total investment was down 41% from 2022, and the number of invested companies down 37%, indicating a difficult financing environment and stricter screening for investment targets. SaaS accounted for 18% of startup investment in Japan, which totaled JPY 753.6 bn in 2023, a smaller share compared to the previous year.
On the other hand, financing rounds are increasing in scale. The median investment per startup was up 34% YoY, especially in Series A and other early-stage cases. This trend is especially prominent when a serial entrepreneur sets out to finance their next startup.
<Vertical SaaS>
6. Vertical SaaS / Private Companies: While large-scale financing is limited, many startups are steadily raising funds and gaining presence.
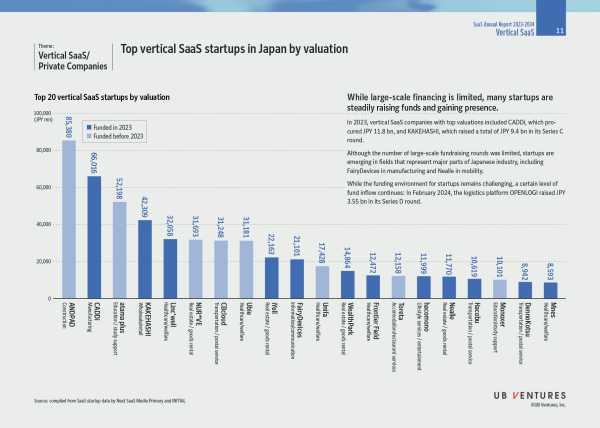
In 2023, vertical SaaS companies with top valuations included CADDi, which procured JPY 11.8 bn, and KAKEHASHI, which raised a total of JPY 9.4 bn in its Series C round.
Although the number of large-scale fundraising rounds was limited, startups are emerging in fields that represent major parts of Japanese industry, including FairyDevices in manufacturing and Nealle in mobility.
While the funding environment for startups remains challenging, a certain level of fund inflow continues: In February 2024, the logistics platform OPENLOGI raised JPY 3.55 bn in its Series D round.
7. Vertical SaaS Financing: Investment increased in vertical SaaS that tackle the “2024 problem.” CADDi leads large-scale financing in the manufacturing industry.
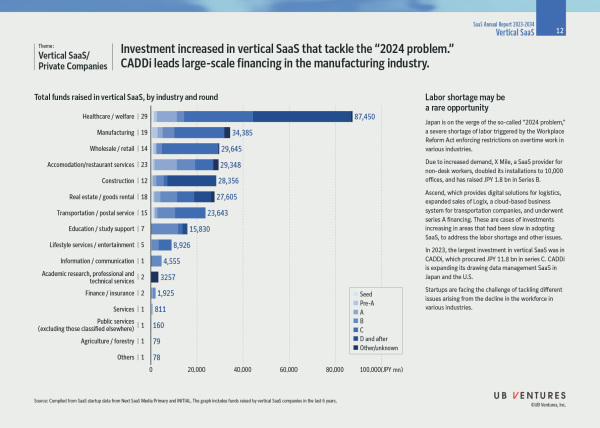
Japan is on the verge of the so-called “2024 problem,” a severe shortage of labor triggered by the Workplace Reform Act enforcing restrictions on overtime work in various industries.
Startups are standing up to the challenge of tackling different issues arising from the workforce decline in various industries.
Due to increased demand, X Mile, a SaaS provider for non-desk workers, doubled its installations to 10,000 offices, and has raised JPY 1.8 bn in Series B.
Ascend, which provides digital solutions for logistics, expanded sales of Logix, a cloud-based business system for transportation companies, and underwent series A financing. These are cases of investments increasing in areas that had been slow in adopting SaaS, to address the labor shortage and other issues.
In 2023, the largest investment in vertical SaaS was in CADDi, which procured JPY 11.8 bn in series C. CADDi is expanding its drawing data management SaaS in Japan and the U.S.
<Depopulating Society>
8. Depopulating Society: With the working population deficit proceeding, as evident in the 2024 problem, the question is how to improve labor productivity and increase the workforce
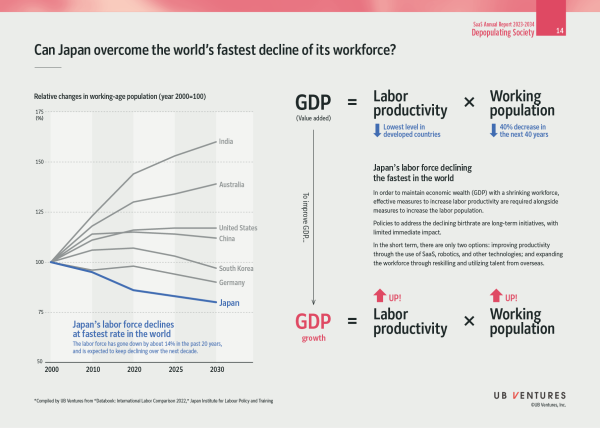
In order to maintain economic wealth (GDP) with a shrinking workforce, effective measures to increase labor productivity are required alongside measures to increase the labor population.
Policies to address the declining birthrate are long-term initiatives, with limited immediate impact. In the short term, there are only two options: improving productivity through the use of SaaS, robotics, and other technologies; and expanding the workforce through reskilling and utilizing talent from overseas.
9. Areas of focus in depopulation: Eight key themes to improve labor productivity and boost working population

10. Startups tackling depopulation: Emerging players in vertical domains providing solutions for operational efficiency

Download full report (free) / Disclaimer
You can download the full report (24 pages) by submitting the form below.
We are committed to managing and protecting your personal information we receive in the manner stated below. By continuing, you agree to the following:
[Collection, Use, and Provision of Personal Information]
UB Ventures, Inc. (“the Company”) may use your personal information to send you this report, to inform you of our next content release, to distribute our email newsletter, to invite you to events hosted by us, to identify and consider potential portfolio companies and LPs, and to respond to your inquiries.
[Provision of Personal Information to Third Parties]
The Company will not provide your personal information to any third party, except with your consent or in accordance with laws and regulations.
[Personal Information Protection Policy]
Please refer to the following link for details of the Company’s personal information management.
UB Ventures, Inc.
Overall direction
Representative Director Managing Partner Osamu Iwasawa
Chief Analyst Akio Hayafune
Principal Takuya Oshika
Editing, Research, Production Assistance
Senior Associate Shinya Iwashita
Entrepreneur-in-Residence Takuya Maehashi
Intern Atsushi Kawazoe
Design
Hajime Aomatsu (sukku)
Interviewees
Mr. Kazuhiro Imamura, CSO, SystemForest inc.
Mr. Gafar Ahmed, CEO and Founder, AIR VISA Inc.
Mr. Hiroki Nozaki, CEO, SoftRoid Inc.
Translation
Makiko Migiyama
Data Reference
INITIAL: https://initial.inc/
Next SaaS Media Primary: https://note.com/_funeo
Here at UB Ventures, we regularly deliver useful content on both Japanese and global startup trends, as well as hands-on experience from our very own venture capitalists and specialists. Please feel free to contact us via the CONTACT page if you would like to be in touch. Click here to follow UB Venture’s SNS account!
-
SCALING
METRICS
TRENDS
SaaS Annual Report 2023-2024
-
SCALING
METRICS
TRENDS
SaaS Annual Report 2022 – The Key to Industry Transformation –
-
TRENDS
Will the next Unicorn Emerge from the Industrial IoT market in Japan?
-
TRENDS
Will hanko seals ever disappear from Japan?
-
TRENDS
System Integrators – the Key to Success for SaaS in Japan
-
SCALING
Has SaaS become a recognized industry in Japan?
-
SCALING
A list of “Don’ts” when building SaaS: Lessons learnt from engaging with 200 startups
-
SCALING
METRICS
TRENDS
SaaS Annual Report 2021
-
SCALING
TRENDS
3 Successful Strategies of Top Logistics Startups in SEA
-
TRENDS
SEA-Specific Vertical SaaS
-
TRENDS
Latest SaaS Trends in SEA
-
TRENDS
The State of Vertical SaaS in Japan
